 |
| A thunderstorm with
heavy precipitation. |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the
condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under
gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of
precipitation include drizzling, rain, sleet, snow, ice
pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a
portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water
vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the
water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog
and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the
water vapor does not condense sufficiently to
precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together,
can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or
adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as
smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain
drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense
periods of rain in scattered locations are called
showers.
Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over
a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be
condensed into clouds and rain. This process is
typically active when freezing rain occurs. A stationary
front is often present near the area of freezing rain
and serves as the focus for forcing and rising air.
Provided there is necessary and sufficient atmospheric
moisture content, the moisture within the rising air
will condense into clouds, namely nimbostratus and
cumulonimbus if significant precipitation is involved.
Eventually, the cloud droplets will grow large enough to
form raindrops and descend toward the Earth where they
will freeze on contact with exposed objects. Where
relatively warm water bodies are present, for example
due to water evaporation from lakes, lake-effect
snowfall becomes a concern downwind of the warm lakes
within the cold cyclonic flow around the backside of
extratropical cyclones. Lake-effect snowfall can be
locally heavy. Thundersnow is possible within a
cyclone's comma head and within lake effect
precipitation bands. In mountainous areas, heavy
precipitation is possible where upslope flow is
maximized within windward sides of the terrain at
elevation. On the leeward side of mountains, desert
climates can exist due to the dry air caused by
compressional heating. Most precipitation occurs within
the tropics and is caused by convection. The movement of
the monsoon trough, or intertropical convergence zone,
brings rainy seasons to savannah regions.
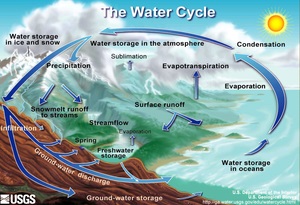
Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle,
and is responsible for depositing the fresh water on the
planet. Approximately 505,000 cubic kilometres (121,000
cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year:
398,000 cubic kilometres (95,000 cu mi) over oceans and
107,000 cubic kilometres (26,000 cu mi) over land. Given
the Earth's surface area, that means the globally
averaged annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39
in), but over land it is only 715 millimetres (28.1 in).
Climate classification systems such as the Köppen
climate classification system use average annual
rainfall to help differentiate between differing climate
regimes.
Precipitation may occur on other celestial bodies.
Saturn's largest satellite, Titan, hosts methane
precipitation as a slow-falling drizzle, which has been
observed as Rain puddles at its equator and polar
regions. |
|
 |
| Condensation and
coalescence are important parts of the water
cycle. |
Types
Precipitation is a major component of the water cycle,
and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh
water on the planet. Approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000
mi3) of water falls as precipitation each year, 398,000
km3 (95,000 cu mi) of it over the oceans. Given the
Earth's surface area, that means the globally averaged
annual precipitation is 990 millimetres (39 in).
Mechanisms of producing precipitation include
convective, stratiform, and orographic rainfall.
Convective processes involve strong vertical motions
that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that
location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation,
while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions
and less intense precipitation. Precipitation can be
divided into three categories, based on whether it falls
as liquid water, liquid water that freezes on contact
with the surface, or ice. Mixtures of different types of
precipitation, including types in different categories,
can fall simultaneously. Liquid forms of precipitation
include rain and drizzle. Rain or drizzle that freezes
on contact within a subfreezing air mass is called
"freezing rain" or "freezing drizzle". Frozen forms of
precipitation include snow, ice needles, ice pellets,
hail, and graupel. |
|
Forms of precipitation
Raindrops
Coalescence occurs when water droplets fuse to create
larger water droplets, or when water droplets freeze
onto an ice crystal, which is known as the Bergeron
process. The fall rate of very small droplets is
negligible, hence clouds do not fall out of the sky;
precipitation will only occur when these coalesce into
larger drops. When air turbulence occurs, water droplets
collide, producing larger droplets. As these larger
water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that
drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and
fall as rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from 0.1 millimetres
(0.0039 in) to 9 millimetres (0.35 in) mean diameter,
above which they tend to break up. Smaller drops are
called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As
a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more
oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the
oncoming airflow. Contrary to the cartoon pictures of
raindrops, their shape does not resemble a teardrop.
Intensity and duration of rainfall are usually inversely
related, i.e., high intensity storms are likely to be of
short duration and low intensity storms can have a long
duration. Rain drops associated with melting hail tend
to be larger than other rain drops. The METAR code for
rain is RA, while the coding for rain showers is SHRA.
Ice pellets
Ice pellets or sleet are a form of precipitation
consisting of small, translucent balls of ice. Ice
pellets are usually (but not always) smaller than
hailstones. They often bounce when they hit the ground,
and generally do not freeze into a solid mass unless
mixed with freezing rain. The METAR code for ice pellets
is PL.
Ice pellets form when a layer of above-freezing air
exists with sub-freezing air both above and below. This
causes the partial or complete melting of any snowflakes
falling through the warm layer. As they fall back into
the sub-freezing layer closer to the surface, they
re-freeze into ice pellets. However, if the sub-freezing
layer beneath the warm layer is too small, the
precipitation will not have time to re-freeze, and
freezing rain will be the result at the surface. A
temperature profile showing a warm layer above the
ground is most likely to be found in advance of a warm
front during the cold season, but can occasionally be
found behind a passing cold front.
Hail
Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm clouds
when supercooled water droplets freeze on contact with
condensation nuclei, such as dust or dirt. The storm's
updraft blows the hailstones to the upper part of the
cloud. The updraft dissipates and the hailstones fall
down, back into the updraft, and are lifted again. Hail
has a diameter of 5 millimetres (0.20 in) or more.
Within METAR code, GR is used to indicate larger hail,
of a diameter of at least 6.4 millimetres (0.25 in). GR
is derived from the French word grêle. Smaller-sized
hail, as well as snow pellets, use the coding of GS,
which is short for the French word grésil. Stones just
larger than golf ball-sized are one of the most
frequently reported hail sizes. Hailstones can grow to
15 centimetres (6 in) and weigh more than 500 grams (1
lb). In large hailstones, latent heat released by
further freezing may melt the outer shell of the
hailstone. The hailstone then may undergo 'wet growth',
where the liquid outer shell collects other smaller
hailstones. The hailstone gains an ice layer and grows
increasingly larger with each ascent. Once a hailstone
becomes too heavy to be supported by the storm's
updraft, it falls from the cloud.
Snowflakes
Snow crystals form when tiny supercooled cloud droplets
(about 10 μm in diameter) freeze. Once a droplet has
frozen, it grows in the supersaturated environment.
Because water droplets are more numerous than the ice
crystals the crystals are able to grow to hundreds of
micrometers in size at the expense of the water
droplets. This process is known as the Wegener–Bergeron–Findeisen
process. The corresponding depletion of water vapor
causes the droplets to evaporate, meaning that the ice
crystals grow at the droplets' expense. These large
crystals are an efficient source of precipitation, since
they fall through the atmosphere due to their mass, and
may collide and stick together in clusters, or
aggregates. These aggregates are snowflakes, and are
usually the type of ice particle that falls to the
ground. Guinness World Records list the world's largest
snowflakes as those of January 1887 at Fort Keogh,
Montana; allegedly one measured 38 cm (15 inches) wide.
The exact details of the sticking mechanism remain a
subject of research.
Although the ice is clear, scattering of light by the
crystal facets and hollows/imperfections mean that the
crystals often appear white in color due to diffuse
reflection of the whole spectrum of light by the small
ice particles. The shape of the snowflake is determined
broadly by the temperature and humidity at which it is
formed. Rarely, at a temperature of around −2 °C (28
°F), snowflakes can form in threefold
symmetry—triangular snowflakes. The most common snow
particles are visibly irregular, although near-perfect
snowflakes may be more common in pictures because they
are more visually appealing. No two snowflakes are
alike, as they grow at different rates and in different
patterns depending on the changing temperature and
humidity within the atmosphere through which they fall
on their way to the ground. The METAR code for snow is
SN, while snow showers are coded SHSN.
Diamond dust
Diamond dust, also known as ice needles or ice crystals,
forms at temperatures approaching −40 °C (−40 °F) due to
air with slightly higher moisture from aloft mixing with
colder, surface-based air. They are made of simple ice
crystals, hexagonal in shape. The METAR identifier for
diamond dust within international hourly weather reports
is IC.
Causes
Frontal activity
Stratiform or dynamic precipitation occurs as a
consequence of slow ascent of air in synoptic systems
(on the order of cm/s), such as over surface cold
fronts, and over and ahead of warm fronts. Similar
ascent is seen around tropical cyclones outside of the
eyewall, and in comma-head precipitation patterns around
mid-latitude cyclones. A wide variety of weather can be
found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms
possible, but usually their passage is associated with a
drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts usually form
around mature low-pressure areas. Precipitation may
occur on celestial bodies other than Earth. When it gets
cold, Mars has precipitation that most likely takes the
form of ice needles, rather than rain or snow. |
 |
| Convective
precipitation. |
Convection
Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from
convective clouds, e.g. cumulonimbus or cumulus
congestus. It falls as showers with rapidly changing
intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain
area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds
have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in
the tropics appears to be convective; however, it has
been suggested that stratiform precipitation also
occurs. Graupel and hail indicate convection. In
mid-latitudes, convective precipitation is intermittent
and often associated with baroclinic boundaries such as
cold fronts, squall lines, and warm fronts. |
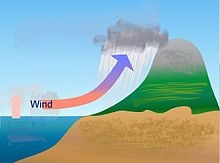 |
| Orographic
precipitation. |
Orographic
effects
Orographic precipitation occurs on the windward (upwind)
side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion
of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain
ridge, resulting in adiabatic cooling and condensation.
In mountainous parts of the world subjected to
relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade
winds), a more moist climate usually prevails on the
windward side of a mountain than on the leeward or
downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift,
leaving drier air (see katabatic wind) on the descending
and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow
is observed.
In Hawaii, Mount Waiʻaleʻale, on the island of Kauai, is
notable for its extreme rainfall, as it has the
second-highest average annual rainfall on Earth, with
12,000 millimetres (460 in). Storm systems affect the
state with heavy rains between October and March. Local
climates vary considerably on each island due to their
topography, divisible into windward (Koʻolau) and
leeward (Kona) regions based upon location relative to
the higher mountains. Windward sides face the east to
northeast trade winds and receive much more rainfall;
leeward sides are drier and sunnier, with less rain and
less cloud cover.
In South America, the Andes mountain range blocks
Pacific moisture that arrives in that continent,
resulting in a desertlike climate just downwind across
western Argentina. The Sierra Nevada range creates the
same effect in North America forming the Great Basin and
Mojave Deserts. Similarly, in Asia, the Himalaya
mountains create an obstacle to monsoons which leads to
extremely high precipitation on the southern side and
lower precipitation levels on the northern side. |
|