|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
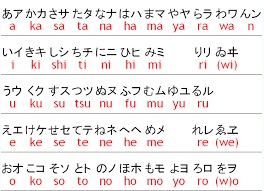 |
| Table showing the
Japanese basic sounds written in hiragana,
katakana, and romaji. |
Romaji
The romanization of Japanese is the use of Latin script
to write the Japanese language. This method of writing
is sometimes referred to in Japanese as rōmaji (ローマ字,
literally, "Roman letters"; [ɾoːma(d)ʑi] (About this
soundlisten) or [ɾoːmaꜜ(d)ʑi]). There are several
different romanization systems. The three main ones are
Hepburn romanization, Kunrei-shiki romanization (ISO
3602), and Nihon-shiki romanization (ISO 3602 Strict).
Variants of the Hepburn system are the most widely used. |
|
|
Japanese is normally written in a combination of
logographic characters borrowed from Chinese (kanji) and
syllabic scripts (kana) that also ultimately derive from
Chinese characters. Rōmaji may be used in any context
where Japanese text is targeted at non-Japanese speakers
who cannot read kanji or kana, such as for names on
street signs and passports, and in dictionaries and
textbooks for foreign learners of the language. It is
also used to transliterate Japanese terms in text
written in English (or other languages that use the
Latin script) on topics related to Japan, such as
linguistics, literature, history, and culture. Rōmaji is
the most common way to input Japanese into word
processors and computers, and may also be used to
display Japanese on devices that do not support the
display of Japanese characters. |
|
|
All Japanese who have attended elementary school since
World War II have been taught to read and write
romanized Japanese. Therefore, almost all Japanese are
able to read and write Japanese using rōmaji, although
it is extremely rare in Japan to use this method to
write Japanese (except as an input tool on a computer or
for special purposes like in some logo design), and most
Japanese are more comfortable reading kanji and kana. |
|
History
The earliest Japanese romanization system was based on
Portuguese orthography. It was developed around 1548 by
a Japanese Catholic named Anjirō.[citation needed]
Jesuit priests used the system in a series of printed
Catholic books so that missionaries could preach and
teach their converts without learning to read Japanese
orthography. The most useful of these books for the
study of early modern Japanese pronunciation and early
attempts at romanization was the Nippo jisho, a
Japanese–Portuguese dictionary written in 1603. In
general, the early Portuguese system was similar to
Nihon-shiki in its treatment of vowels. Some consonants
were transliterated differently: for instance, the /k/
consonant was rendered, depending on context, as either
c or q, and the /ɸ/ consonant (now pronounced /h/,
except before u) as f; and so Nihon no kotoba ("The
language of Japan") was spelled Nifon no cotoba. The
Jesuits also printed some secular books in romanized
Japanese, including the first printed edition of the
Japanese classic The Tale of the Heike, romanized as
Feiqe no monogatari, and a collection of Aesop's Fables
(romanized as Esopo no fabulas). The latter continued to
be printed and read after the suppression of
Christianity in Japan (Chibbett, 1977).
Following the expulsion of Christians from Japan in the
late 1590s and early 17th century, rōmaji fell out of
use and was used sporadically in foreign texts until the
mid-19th century, when Japan opened up again.
From the mid-19th century onward, several systems were
developed, culminating in the Hepburn system, named
after James Curtis Hepburn who used it in the third
edition of his Japanese–English dictionary, published in
1887. The Hepburn system included representation of some
sounds that have since changed. For example, Lafcadio
Hearn's book Kwaidan shows the older kw- pronunciation;
in modern Hepburn romanization, this would be written
Kaidan (lit. 'ghost tales'). |
|
|
 Kiddle: Romanization of Japanese Kiddle: Romanization of Japanese
Wikipedia: Romanization of Japanese |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |